In the current era, people literally track which year it is or going to come. You must have heard the term AD or ‘Anno Domini.’ It stands for ‘the Year of the Lord’ in Latin, and that is based on the Gregorian calendar. Interestingly, it has been followed by people for hundreds of years.
You may wonder how humans then track years before following Anno Domini. Or when did we start counting years?
It is believed that when a multicultural society emerged, humans realized the need to synchronize calendars. The professor of Ancient History and academic staff of the Center for the Cultural Heritage and Texts of the Nagoya University, Yoshiyuki Suto, at the second phase of the Intercontinental Academia (ICA), said –
“The setting of time was closely related to the sense of social stability.”
How Did We Start Counting Years?
We accepted and used the units like seconds, minutes, and hours for expressing time. But how do these markers originate? Ever thought of it?
Humans opted for different ways of counting the time before the Gregorian calendar integrated with the Anno Domini calendar period. So let’s delve into it!
1. Ab urbe condita

Ab urbe condita or AUC is a dating system that means “from the founding of the City” in Latin. Here the years are counted from the mythical foundation of Rome. Ancient Roman scholars used ab urbe condita in concurrence with the regnal dating system.
This dating system started from the year Rome was founded; the Roman scholars traditionally counted it as the year 753 BCE.
People then counted 752 BCE as 1 AUC or a year since Rome’s foundation. This system was acknowledged universally. And you will be fascinated to know that Rome’s millennium was commemorated by the Roman Emperor Philip the Arab in 248CE. So now people label this year as 1000 AUC, which is a whole millennium since the foundation of Rome.
However, Roman Emperor Philip celebrated this occasion wholeheartedly, arranging feasts and manufacturing exclusively minted coins.
Nonetheless, according to this system, our current year AD 2022 would be 2775 AUC.
Also Read:- How to Disconnect Your iPhone From Your Mac in 9 Easy Ways?
2. The Age of Kings

In the era of kings, people used to tie the date to the current emperor, king, or ruler. This popular dating system is apparent in several ancient texts, such as the Bible. The phrase in the passages starts with “in x year of the reign of y ruler,” indicating the place in a particular time.
People kept track and maintained a chart of the reign of rulers and emperors. You will find this practice universally in ancient times. Even the Chinese and Japanese, the Romans, and ancient Jews followed this dating practice. And this is referred to as the regnal year.
Throughout history, people have accepted this system because of many reasons.
It integrated the current king into the counting of time. Eventually, the monarch could acknowledge a strong presence with his people, enjoying the ruling legitimacy.
Moreover, people could easily adopt this system of dating.
From clerks, courts to historians, everybody was already focused on calculating the years of kings. And the process of counting the years was indeed easier as it required no knowledge of learning or using an external system.
However, the fascinating thing to remember is that –
The regnal system of dating does not have a year zero, just like our present BC/AD dating. This is because a king’s reign doesn’t have a zero year. People recorded the king’s first year of reign as year one, then two, then three, etc.
Also Read:- How to Make Your Move to Hawaii Easier
3. The Hebrew Calendar
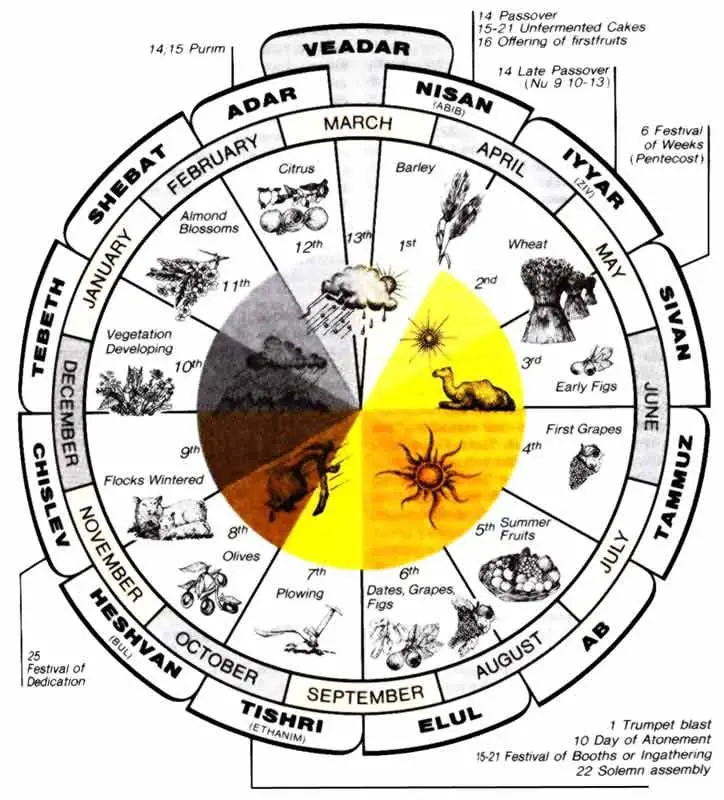
Here is another popular system that humans once accepted to count the years – the Hebrew calendar. Interestingly, it appeared in some form for thousands of years. The Hebrew calendar has the markings of the stringent beliefs of the Jewish faith. It included festivals, special readings from the Torah, and holidays.
However, remember how years are counted in the Roman calendar? Just like that, the Hebrew calendar shows counting years from a foundation time. But here, Rome’s founding is not considered the founding year. Instead, the Hebrew calendar counts years from the world’s foundation, as explained in their sacred texts.
The Jewish culture even has other systems of dating where the counting of years begins since the demolition of the First Temple. The years of rebuilding and demolition of the Second Temple are also considered. Moreover, Anno Mundi is the current system that counts the years from when people accepted that God created the Earth.
‘Anno Mundi’ refers to the ‘creation or from the world’ in Latin. So the starting of the year 2022 in the Gregorian calendar means the year AM 5782 in the Jewish calendar.
Also Read:- 7 Tips to Write A Formal Letter on Lined Paper
4. The Modern system
The interesting fact about our current system is that scholars and more secular-minded people have converted the Before Christ (B.C) and Anno Domini (AD) era dating system into Before Current Era (BCE) and Current Era (CE). They did it to detract people from using the birth of Jesus Christ as the year of counting.
However, people started to acknowledge this system universally in the Middle Ages. Then, it gradually started to dominate the Renaissance, integrating with the Gregorian calendar. As time passed, people started to connect and depend on one another for business. And eventually, they realized the urgent need for a standard system of the time.
Over the years, this system of the time was refined and shared in a universal way. Today, it has become a norm for the world to use a single calendar.
Role of the Egyptians in Counting Years

The Egyptians were the first who count annual periods by observing the stars. In addition, these time-masters also made twelve sub-divisions of time depending on the seasons. Herodotus, the Greek geographer, and historian, wrote about them in 3 BC. It is said that the Egyptians had an excellent ability to make calculations, more precise than the Greeks.
They were more precise than the Greeks, who included an intercalary month every two years to make the seasons clash. However, the Egyptians added five days to the total of every year, counting 30 days. Eventually, the entire circle of the seasons and the calendar coincide.
During Hellenism, human history saw the first epoch of globalization. There has been the formation of big empires and large kingdoms, featuring an entirely different time. Moreover, this era is significant because it encountered the expeditions of Alexander the Great to Asia, Rome’s invasion of Eastern Greece, and the expansion of the Greek language.
It was often necessary to record the historical events and public announcements in more than one type of language. Interestingly, different people adopted bishoprics, public documents referencing reigns, and other historical realities based on Egyptian, Sumerian or Greek calendars for preventing errors about the fact or the date. So it was necessary to synchronize time.
Also Read:- How to Write A Check For 1200 Dollars? (A Step-by-Step Guide)
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. When Did Humans First Count Time?
Sundials originated in ancient Egypt in the early 1500 BC, which paved the way for time measurement. But, of course, today’s way we measure time is not the same as the Egyptians did. The period of daylight was the basic unit of time for not only the Egyptians but also for the coming three millennia.
-They divided the time from sunrise to sunrise into twelve parts equally, providing us the predecessor of today’s hours.
-Thus, the hour followed by the Egyptians wasn’t a consistent length of time like we follow today.
-In fact, the Egyptian hour was 1/12th of the daylight, varying with the day length and the seasons.
Furthermore, it also depended on the place on the Earth’s surface. And hours of darkness were not considered, keeping in mind that time is a measurable concept.
Q2. Did the year 666 exist?
Yes, the year 666 was a common period you can identify as Thursday on the Julian calendar. However, you will find the use of the denomination 666 since the early medieval era. This is because it was the time when Europeans commonly accepted the Anno Domini calendar to name the years.
Q3. Why is the year 666 BC historically significant?
The year 666 BC marks the resignation of the King Ashurbanipal of Assyria. While a mock king replaced him, court astrologers forecasted doom upon Assyria.
Q4. What were the years referred to before it was named BC?
The eras BC and AD are often referred to as BCE (Before the Common Era) and CE (Common Era). This is because people in 753 BC used Ab urbe condita or ‘from the foundation of the city’s dating system and continued to follow it until the Anno Domini calendar made its way in AD 525.
Q5. What calendar did people use in Jesus’ time?
The Hebrew calendar was universally acknowledged during Jesus’ time. However, the fascinating fact is that this calendar is a lunisolar calendar. This signifies that the years of this calendar are according to solar years, but months are on lunar months.
Q6. When did humans start to number years?
Humans first calculated the dating ‘Anno Dating’ in 525. It was gradually acknowledged in Western Europe in the 18th century. Still, many places around the globe accept the numbering of years of each Christian era.
